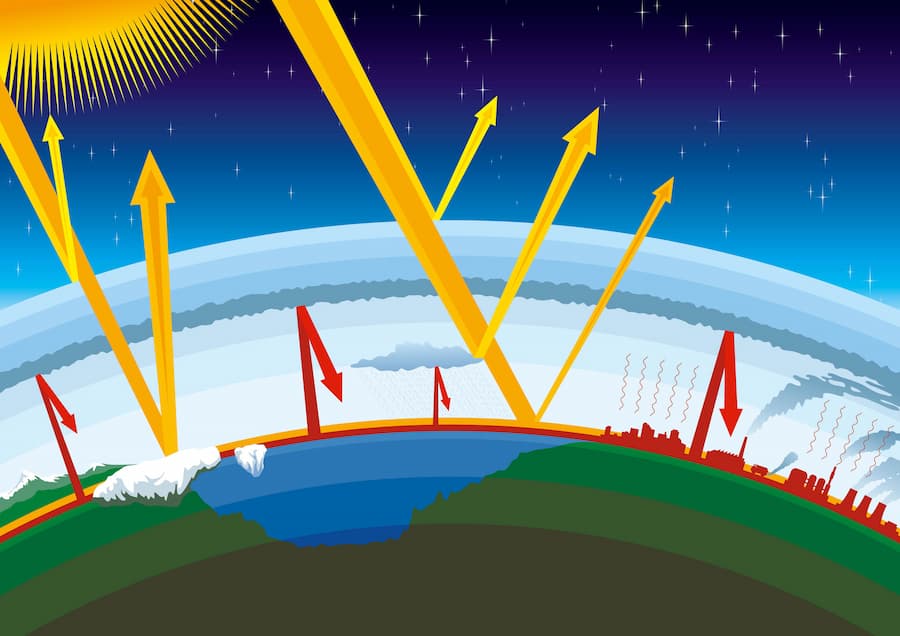
The Greenhouse Effect
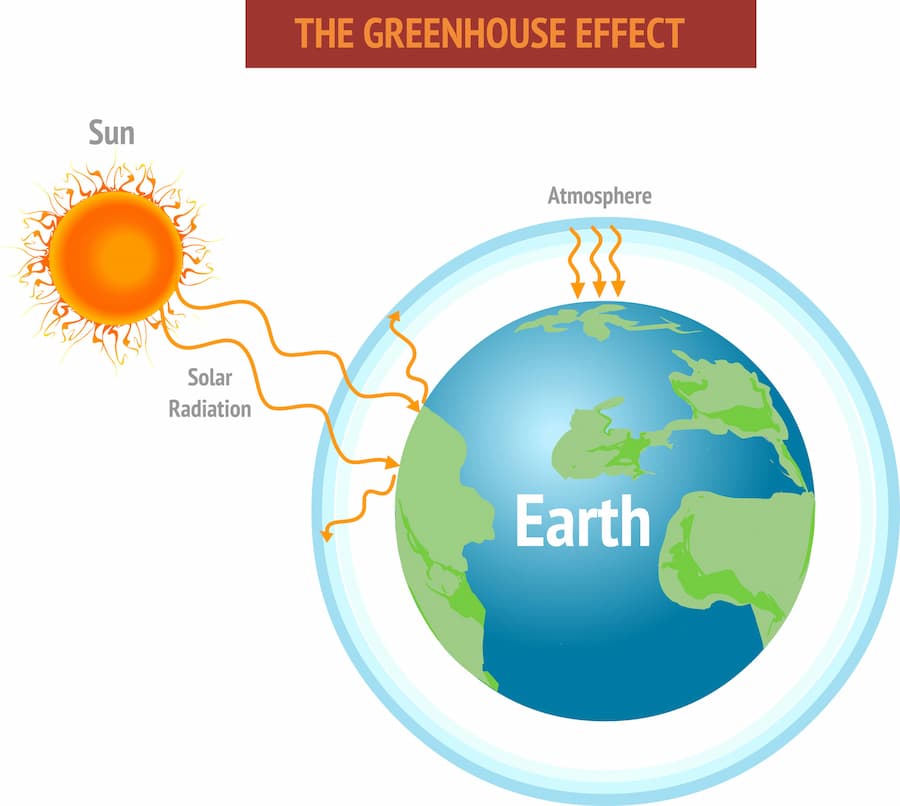
What is the greenhouse effect?
To explain this phenomenon, we need to compare it to a greenhouse.
A greenhouse is a structure where plants are grown.
In these structures, you could grow plants more quickly because of their glass or plastic walls, which trap heat from the sun.
Similarly, the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere trap heat caused by the sun's radiation.
The greenhouse effect has been well understood for more than a century. As a matter of fact, in 1859, British physicist John Tyndall made laboratory experiments that showed that carbon dioxide absorbs heat, thus warming the Earth's surface like a blanket (Source).
The leading gases that trap this heat are known as greenhouse gases. You may have already heard about some of them, particularly carbon dioxide.

Other Greenhouse Gases
The other greenhouse gases include:
- Chlorofluorocarbons
- Hydrochlorofluorocarbons
- Hydrofluorocarbons
- Methane
- Nitrous Oxide
- Ozone
- Perfluorocarbons
- Sulfur Hexafluoride
- Water Vapour
Carbon Dioxide: The Main Greenhouse Gas
The reason for which you probably heard of carbon dioxide is that it is the most crucial one.
Why? The amounts of carbon dioxide have drastically increased in the last two hundred years due to industrialization and are the leading cause of global warming.
To reduce our environmental impact, we must decrease our carbon footprint.

Isn't Carbon Dioxide Natural?
Now you may believe that the greenhouse effect is a bad thing.
However, it is not. Instead, it is essential for life here on Earth and exists naturally. In effect, if all the heat of the sun were sent back into space, there would be no life on Earth (or at least very little).
The problem arises when there is a substantial increase of greenhouse gases in a brief period.

Natural Fluctuations
Over thousands of years, the amount of carbon dioxide increases and decreases. Life on Earth could quickly adapt to this natural fluctuation.
Moreover, the level of carbon dioxide changes from season to season.
During summer and spring, plants take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen through photosynthesis.
In retrospect, when winter arrives, plants release their carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere.
So as you can see, it is typical for concentrations of carbon dioxide to change over time but only to a certain extent.

Very Rapid Increase
So what is a very short period of time? Well, when considering the carbon dioxide levels over the last 800,000 years, they have never exceeded 300 ppm (parts per million) (Source).
In the last 200 years, they went from about 280 to 413 ppm; that is an incredibly fast increase, especially in geological terms (Source).
With the rate it has been increasing over the last 200 years, organisms could not adapt. Many are on the brink of extinction or have already gone extinct.
In fact, ocean acidification is occurring due to the increased amounts of carbon dioxide in our oceans, which will, in turn, fundamentally affect all marine life by endangering species at the bottom of the ocean food chain.

Other Greenhouse Gases
It should also be noted that the other greenhouse gases play a role even though it is smaller. However, in the near future, they could accelerate the effects of climate change.
A great example would be the methane trapped in the permafrost in the Northern Hemisphere, particularly in Canada and Russia.
Feedback Mechanism of Permafrost
With global warming, this permafrost will melt, and massive amounts of methane will be released, causing even more increases in temperatures.
This, in turn, will cause more methane to melt and this creates a terrible snowball effect.
This snowball effect is one of many that will take place.
For more information, see the feedback mechanism.
Other Snowball Effects
As glaciers and the polar ice caps melt, less sunlight is reflected (the color white reflects light), and thus the melting will accelerate.
As the polar ice caps and the massive ice shelves in Antarctica melt, the waters around them will warm up and accelerate this melting even more.
The greenhouse effect is much more alarming than it first appears, especially if you do not take these feedback mechanisms into account.
Troubling Trends of the Greenhouse Effect
Not only is the amount of carbon dioxide that we release into the atmosphere accelerating, but so is the increase in global temperatures.
Result? People simply don't realize this acceleration effect and thus don't understand how dire the situation is.
So now you may ask, what will happen if the planet simply warms up? Will we just have more beautiful summers? Not exactly.
The greenhouse effect has much more severe consequences.
To learn about them, proceed to the effects of climate change.
Further Reading and Sources

Video from 2007
Join the Community and Newsletter (5000 Subscribers)
You can subscribe to my Substack Page or see the archives of previous posts. More great content coming soon!
Recent Articles
-
Climate Change Guide
Apr 23, 24 12:36 PM
The Climate Change Guide is your guide to a more sustainable future, and will provide you with all relevant information on mankind's greatest challenge. -
Climate Presentations by Climate Reality
Mar 03, 24 12:17 AM
You can see great climate presentations by Climate Reality. They can be customized for different audiences. -
Make the Planet Great Again!
Mar 02, 24 11:33 PM
We need to make the planet great again! We will build a solar wall along the Mexican border and make the fossil fuel industry pay for it! -
Historical Climate Change News
Mar 02, 24 11:25 PM
This section includes historical climate change news you should know about. These articles span several different topics and will help you stay up-to-date.